What Is Allowance for Doubtful Accounts? How to Record it?

This is why, for purposes of financial reporting (not tax reporting), companies should use the allowance method rather than the direct write-off method. The Allowance for Doubtful Accounts plays a pivotal role in ensuring that a company’s financial statements present an accurate and fair view of its financial position. By accounting for potential losses from uncollectible receivables, companies can provide a more realistic valuation of their assets, which is critical for effective financial analysis and decision-making. Furthermore, the estimation methods and management practices adopted for this allowance reflect a company’s approach to risk management and financial prudence. The estimated amount of uncollectible accounts receivable is represented in the allowance for doubtful accounts, which is a key accounting concept. This allowance helps to ensure that a company’s financial position is accurately reflected.
How does the allowance method differ from the direct write-off method?
- However, the balance will be back to be normal after adjusting entry for bad debt because the company will add the debit balance to the required balance in the adjusting entry.
- This expense is being reported even though none of the accounts receivables were due in June.
- Construction is notorious for lengthy credit cycles, and collection cycle data reflects this reality.
- Doubtful accounts are considered to be a contra account, meaning an account that reflects a zero or credit balance.
- First, the company debits its AR and credits the allowance for doubtful Accounts.
In this transaction, the debit to Accounts Receivable increases Malloy’s current assets, allowance for doubtful accounts will have an total assets, working capital, and stockholders’ (or owner’s) equity—all of which are reported on its balance sheet. The credit to Service Revenues will increase Malloy’s revenues and net income—both of which are reported on its income statement. The Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is reported on the balance sheet as a contra-asset account, which means it is deducted from the total accounts receivable to reflect the net realizable value of receivables. This presentation ensures that the balance sheet accurately represents the amount of receivables the company expects to collect.

➜ Improve Your Doubtful Account Tracking With Our AR Collections Playbook
- To manage this, businesses using accrual accounting employ an “allowance for doubtful accounts,” a contra-asset account established to estimate future uncollectible amounts.
- In the context of inventory, net realizable value or NRV is the expected selling price in the ordinary course of business minus the costs of completion, disposal, and transportation.
- The first entry reverses the bad debt write-off by increasing Accounts Receivable (debit) and decreasing Bad Debt Expense (credit) for the amount recovered.
- The Allowance Method for Doubtful or Uncollectible Accounts is used to estimate future bad debts based on current month revenues.
- The answer is we use an accounting estimate to get the estimated amount for recording.
- This adjustment provides a clearer picture of the company’s liquidity and operational efficiency.
- It dictates how and when a company should recognize revenue in its financial statements, which has a significant impact on the company’s financial performance and position.
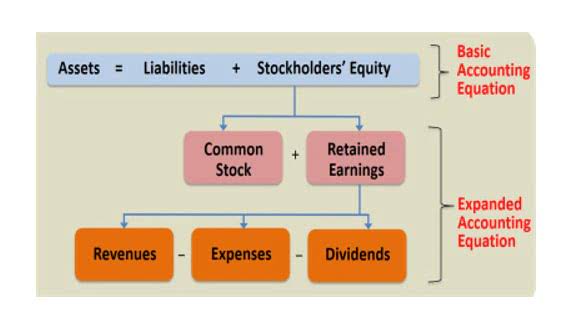
On the balance sheet, an increase is reported in accounts receivable, a decrease is reported in inventory, and a change is reported in stockholders’ equity for the amount of the net income earned on the sale. Companies calculate the allowance for uncollectible accounts using methods like the Percentage of Sales and the Accounts Receivable Aging Method. This methodology ensures that financial statements reflect potential losses accurately, maintaining compliance with accounting standards. Proper record-keeping like this can prevent misstated net incomes and keep financial reporting transparent.
Presentation of Accounts Receivable

To provide a clear financial picture, a company must account for these potential losses. This adjustment ensures financial statements reflect a more accurate representation of assets a company realistically expects to collect. This principle dictates that expenses should be recognized in the same accounting period as the revenues they helped generate, ensuring financial statements accurately reflect profitability. Therefore, the estimated expense of uncollectible accounts is recognized in the period when the related credit sales were made, rather than waiting for specific accounts to become uncollectible. To improve the probability of collection (and avoid bad debts expense) many sellers prepare and mail monthly statements to all customers that have accounts receivable balances.

A bad debt expense occurs when a customer does not pay their invoice for any of the reasons we mentioned earlier. This figure also helps investors estimate the efficiency of a company’s accounts receivable processes. BDE is reported on financial statements using the direct write-off method or the allowance method. Moreover, automated systems can ensure timely reminders for outstanding invoices and facilitate the real-time management of HOA Accounting credit terms and collections. This proactive approach can significantly reduce overdue accounts and prevent bad debts from accumulating. Automation not only optimizes cash flow by ensuring consistent income but also reduces human error and oversight, bringing about more accurate financial reporting.
- For the taxpayer, this means that if a company sells an item on credit in October 2018 and determines that it is uncollectible in June 2019, it must show the effects of the bad debt when it files its 2019 tax return.
- Its Allowance for Doubtful Accounts (before any further adjustment) has a credit balance of $10,000.
- Regular audits and reviews can further strengthen compliance, providing peace of mind and enhancing the company’s reputation with stakeholders.
- This approach can be particularly disruptive for companies with volatile customer payment behaviors.
- To account for potential bad debts, you have to debit the bad debt expense and credit the allowance for doubtful accounts.
- By subtracting this allowance from the total accounts receivable, companies report the “net realizable value” of their receivables, which is the estimated amount they realistically expect to convert into cash.
By predicting the amount of accounts receivables customers won’t pay, you can anticipate your losses from bad debts. This allowance is based on an estimate, often derived from historical collection data, aging of receivables, and economic forecasts. It is a collective provision for future expected losses, not a direct write-off of specific balances. On the balance sheet, AFDA is presented below Accounts Receivable, with its balance subtracted to arrive at the net accounts receivable figure. The adoption of IFRS can https://capitaledgeaccountants.com/?p=7523 lead to more stringent requirements for estimating and reporting bad debts.